Nowadays Linux operating system’s popularity is increasing. Most of the servers are using the Linux Operating System, and personal system also start using various Linux distribution. Ubuntu is one of the popular Linux operating systems.
These days most of the IT professionals learning Linux, as their work environment around Linux based open source and free operating system.
As per my experience, when you are learning anything and for a silly mistake, you are going to format the entire system and reinstall, again and again, the learning period going to be very frustrating and bored.
So, I am suggesting you to at learning time use a virtual environment to configure any Linux and use if any mistake will happen you need to reinstall the only virtual machine, not the system. Or you can keep the previous virtual machine for your experiment to learn to troubleshoot the problem and parallelly you can run new vm to move your learning ahead.
Here, in this article, I am going to explain “How to install Ubuntu 16.04 in VMware workstation?”. You can use any other virtual environment also like Virtualbox, VMware Player, KVM, etc.
Prerequisites – Ubuntu 16.04 installation
Ubuntu 16.04:
Download Ubuntu 16.04 here.
Virtual Environment:
Download VMware Workstation from here.
Download VMware Player from here.
Download Virtualbox from here.
Any application from above is enough for a virtual environment, I am going to use here VMware Workstation, but the overall process of installation is the same for all virtual environment package.
Installing Ubuntu 16.04 in VMware Workstation
Open VMware workstation application to start the installation of Ubuntu 16.04 operating system.
you will get the first screen in workstation like below image, and here click on “Create a New Virtual Machine” button.
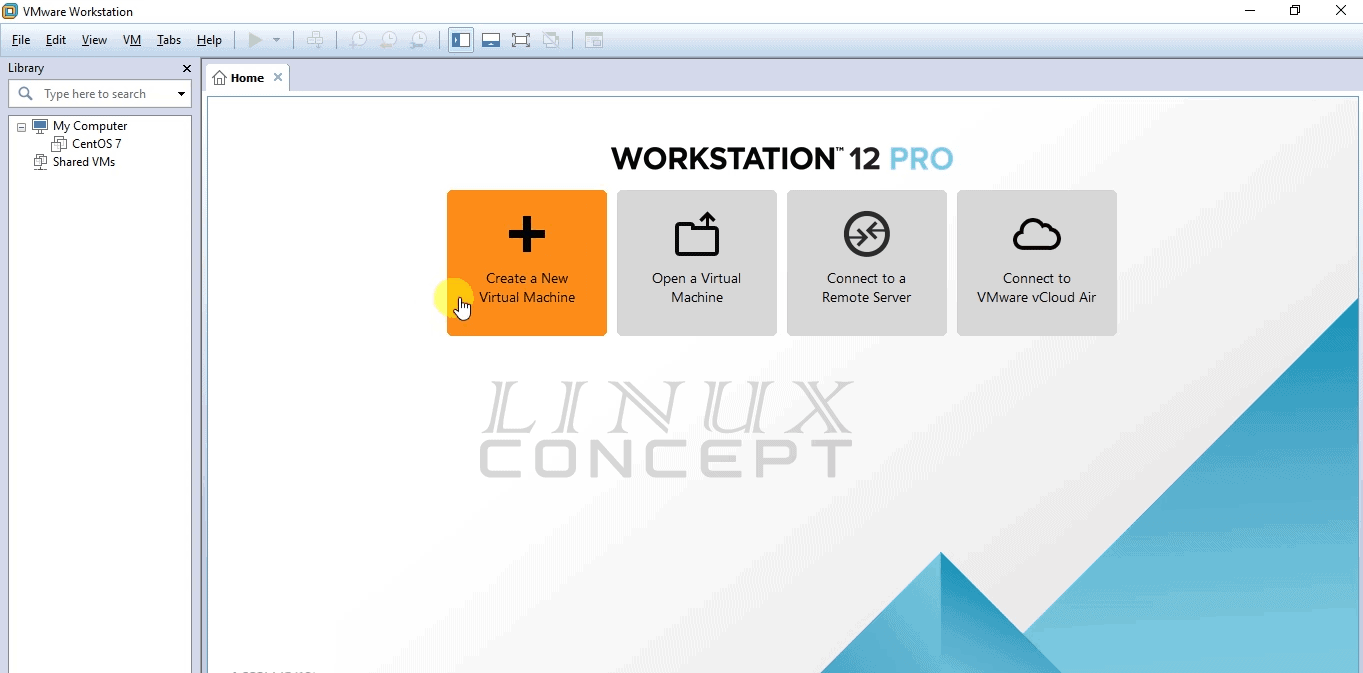
There are two option you will get when start preparing
- Typical (recommended)
- Custom (advanced)
I choose here Custom setup, so can show you all option to configure in VMware.
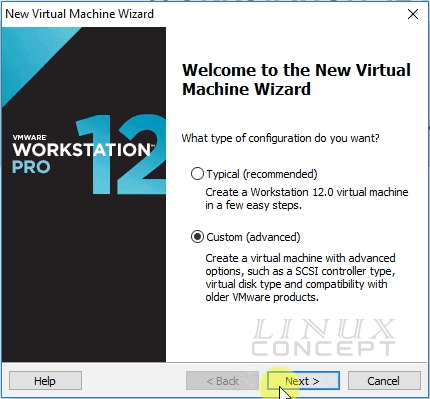
In this window, you can choose hardware compatibility for your virtual machine. As I am using VMware workstation version 12 Pro, so I configured my virtual machine compatibilities according to configured in this version and choose “Workstation 12.0” for Hardware compatibility.
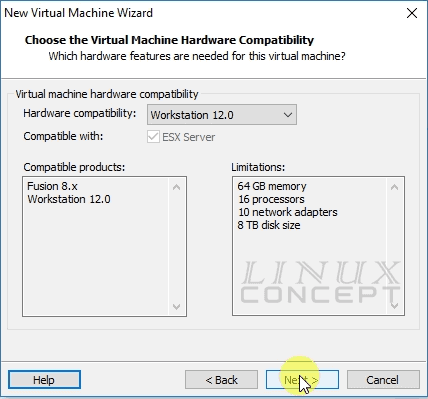
After selection of hardware compatibility, new window will appear for installation media selection, where three options are available:
- Installer disc
- Installer disc image file (iso)
- I will install the operating system later
If you are going to install through operating system CD/DVD disc, you should select “Installer disc”. After selection of this option, you have to select CD/DVD ROM driver.
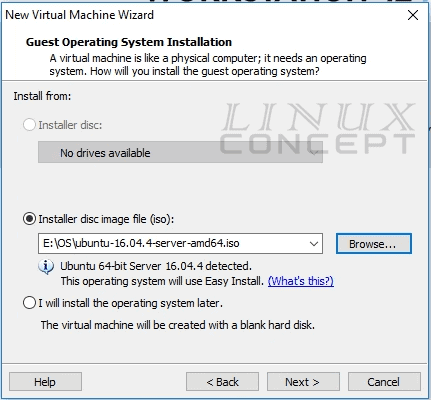
If you are using an operating system iso file, please click on the “Browse” button and select the image file.
If you are just preparing a virtual machine with the configuration where the operating system will install later, just select “I will install the operating system later” option.
Here, I am going to install through iso file, so I choose “Installer disc image file (iso)” and click on the “Browse” button.
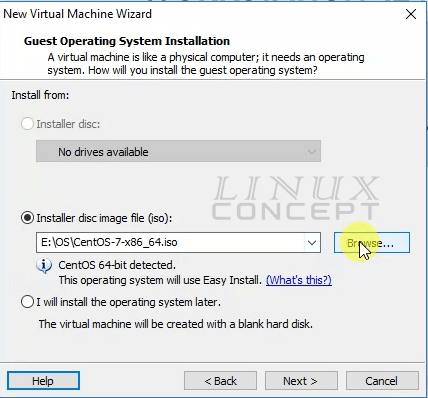
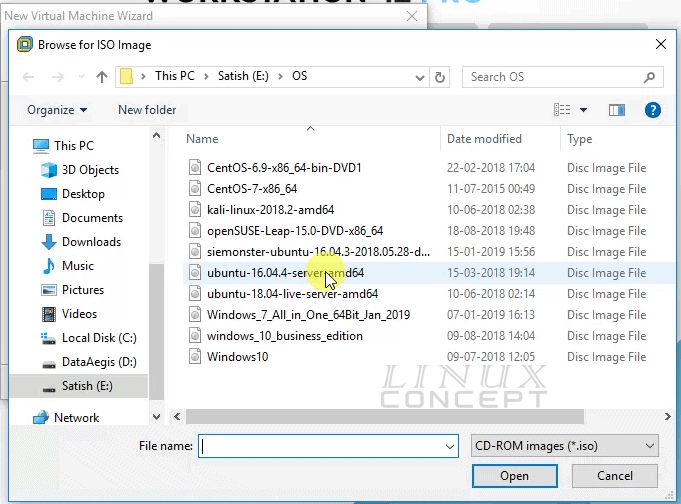
After clicking on “Browser” button a new window will appear, where you need to go to the location of iso file and select the iso file.
Below image showing my all iso file on the location and I am selecting Ubuntu 16.04 operating system’s image file, as I am going to install it.
When you select your operating system disc file it will appear in “installer media selection window” like below image.
Now, click on “Next” button for further configuration.
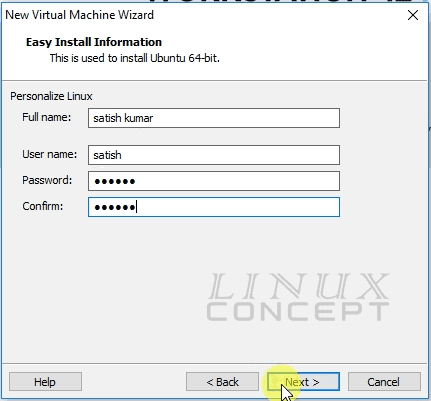
In this window “Personalize Linux” you can fill the form for username and password, which will be on new installed Ubuntu operating system’s default username and password.
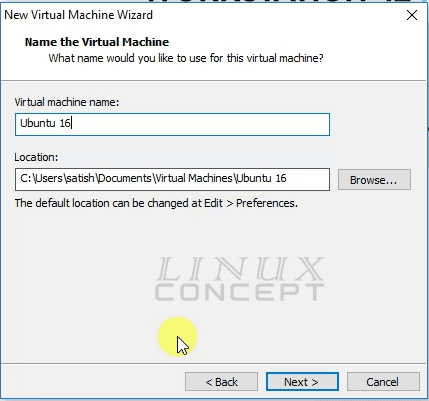
In the next window, you can select the desired name for the virtual machine and location where this virtual machine will store in system storage.
The window will similar like below image.
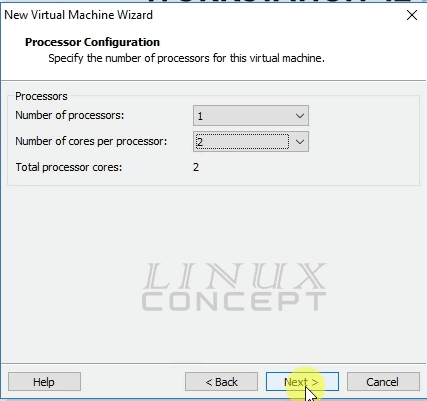
In this window, we configuring processors for the virtual machine.
The options are to select numbers of processors and numbers of cores per processors and after selection of these, click on the “Next” button for further configuration.
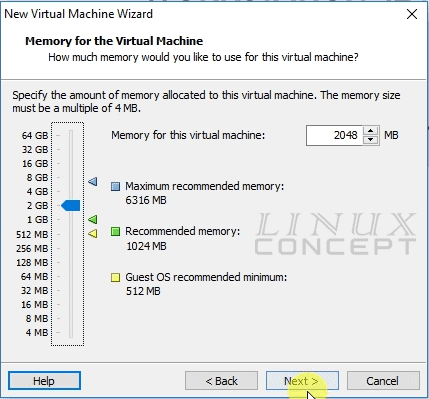
Similarly CPU configuration, in this window we configure RAM for the virtual machine and after selection of RAM quantity click on the “Next” button for further configuration.
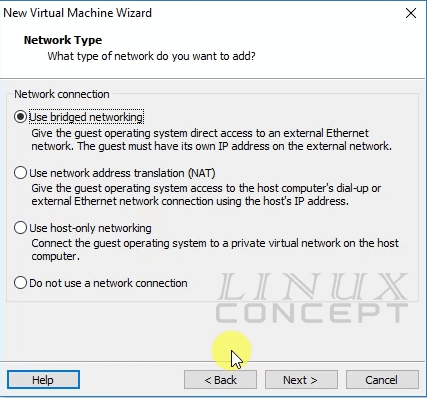
The new window appears for virtual machine network configuration, where we get four option to select like below image;
- Use bridged networking
- Use network address translation (NAT)
- Use host-only networking
- Do not use a network connection
If we want to configure our virtual machine to connect directly with the network and get the IP address from the main network device, we should select “Use bridged networking”.
If we want to configure your networking with our host networking and NAT with the host IP address, we should select “Use network address translation(NAT)”.
Choose “Use host-only networking” if we don’t want to configure independent networking on our virtual machine and use network from the host interface.
The last option “Do not use a network connection” is for if we don’t want to use networking in our virtual machine.
Now, I select “Use bridged networking” as I am using my virtual machine network connectivity directly from the network device without the intervention of the host network.
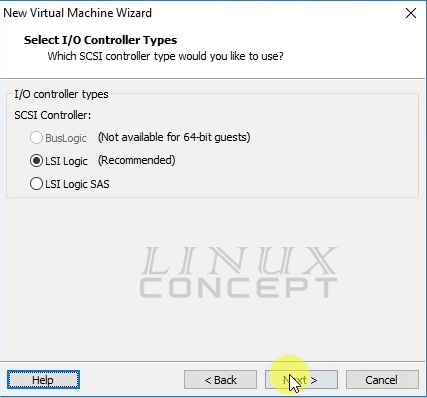
The new window will appear for I/O controller configuration with three option like below image:
- BusLogic
- LSI Logic
- LSI Logic SAS
Bus Logic is not available for the 64-bit arch operating system, and I am using here Ubuntu 16.04 64-bit operating system so it is in disabled mode.
I am not using any SAS device also so not choosing “LSI Logic SAS” option also, so I choose here “LSI Logic” option and click on the “Next” button for further configuration.
Next window is for virtual disk type configuration with options are:
- IDE
- SCSI
- SATA
I suggest choosing the “SCSI” option which is most used by the virtual machine.
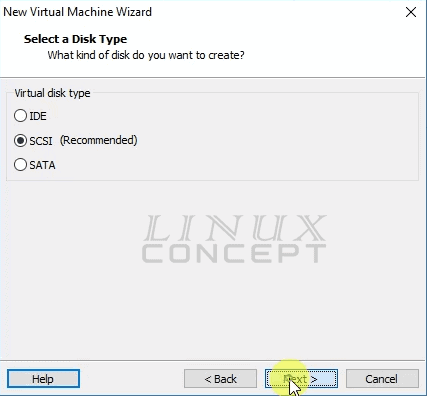
In this window, we are configuring virtual disk with below options:
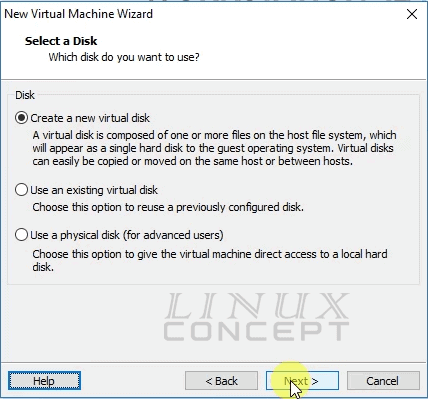
- Create a new virtual disk
- Use an existing virtual disk
- Use a physical disk
Here we will choose “Create a new virtual disk” as we are going to install a new virtual machine.
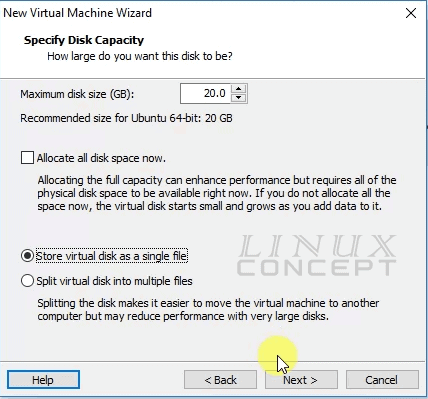
In this window, we are configuring the size of the virtual disk, for this operating system we configured 20 GB as you can see in below image.
If you select “Allocate all disk space now” option it will take all 20 GB storage from the beginning otherwise it will take only storage which is used by the virtual machine.
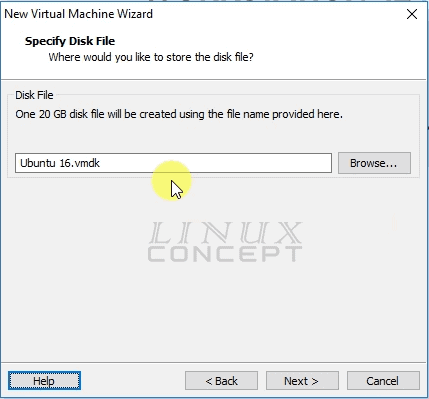
This window is used for naming and locating of the virtual disk file.
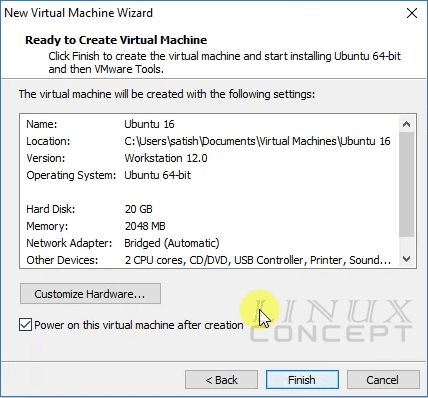
Now, VMware configuration for the new virtual machine is done. this window is summary for all configuration and there is “Customize Hardware…” button which you can use for reconfiguration of any hardware configuration like CPU, RAM etc.
Now Click on “Next” button to finish the virtual machine configuration.
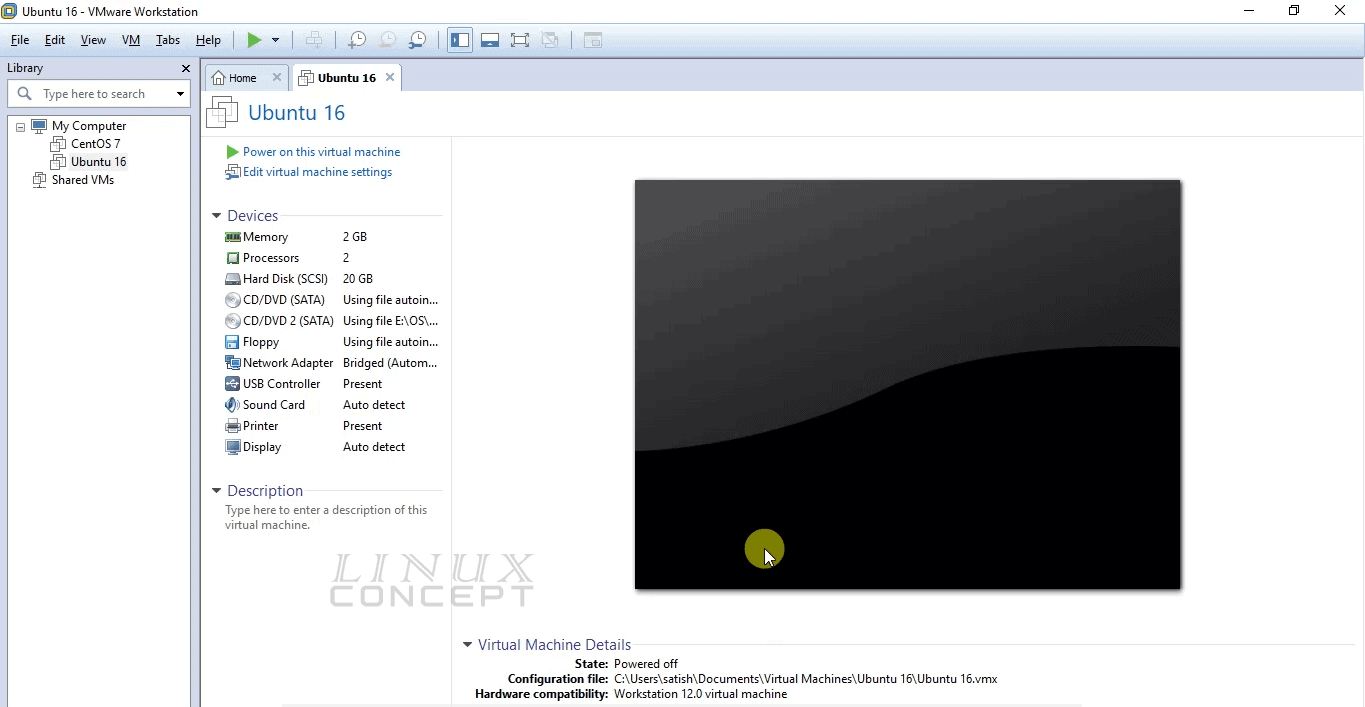
Now, VMware workstation main window will appear with a new tab of new virtual machine “Ubuntu 16”.
Here, click on the “Power on this virtual machine” link to start the virtual machine.
After starting virtual machine you will get below window which is virtual machine booting and VMware logo displaying at booting time.

This new window showing now our new virtual machine booting with Ubuntu installation media and it is ready to install.
In the next screen, the system starts scanning for CD-ROM, which is just checking ISO file or any chosen installation media.

Next screen will appear with “Loading additional component” which is the part of Ubuntu installation.
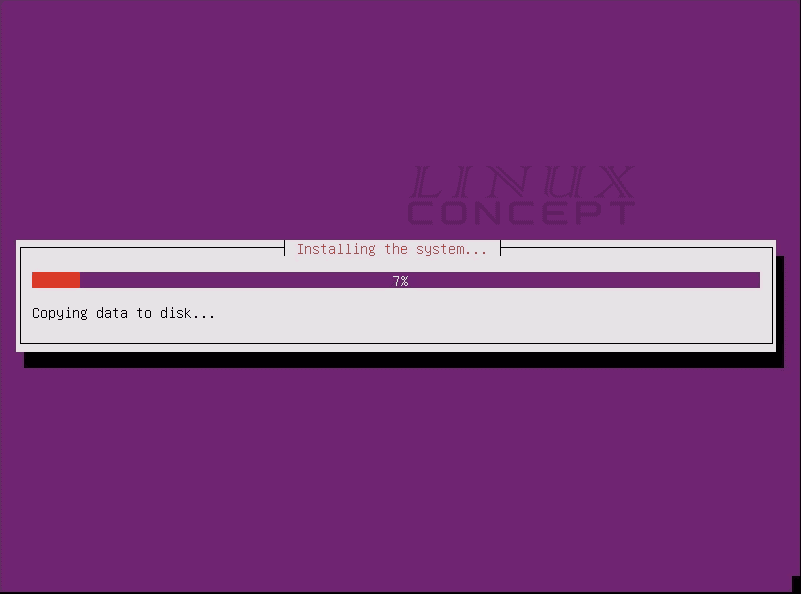
Now, we will get the new screen for “Installing the system” which indicate ubuntu 16.04 operating system installation on the virtual machine is started.
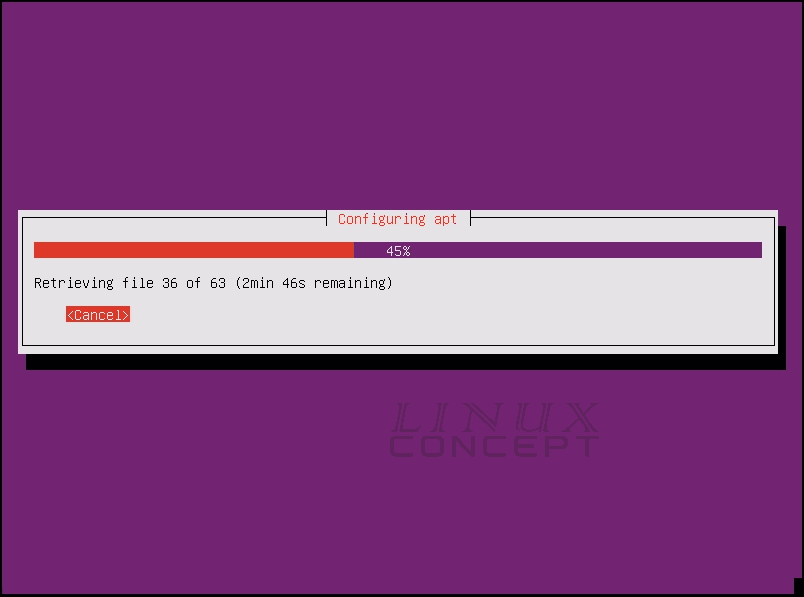
The next screen will appear for “Configuring apt”, apt is the application package manager which is used in Ubuntu operating system. The system starts configuring apt package manager, so if any package required for the operating system it can configure easily.
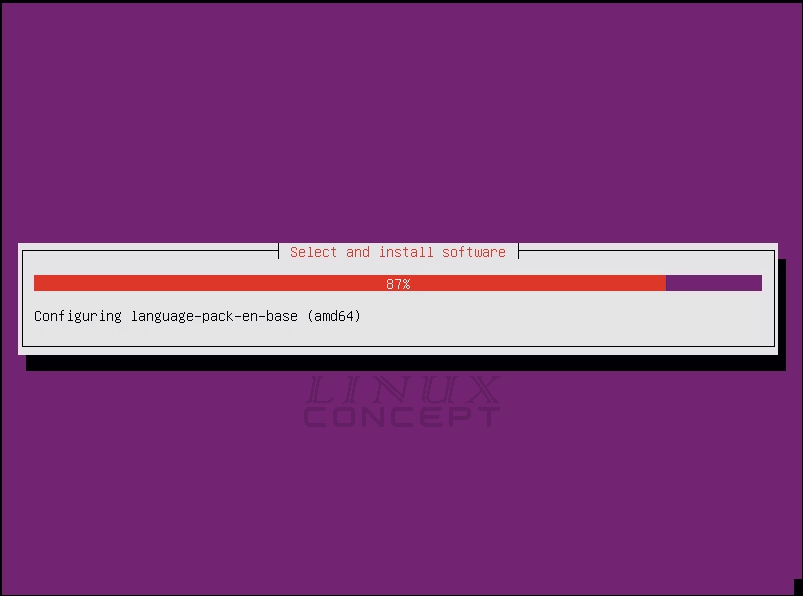
Now, we get a new window for “select and install software”, in this stem all application required by the operating system is installing in the virtual machine.
Now, after installation of the operating system is starts configuring GRUB boot loader for configuring boot device for the operating system.
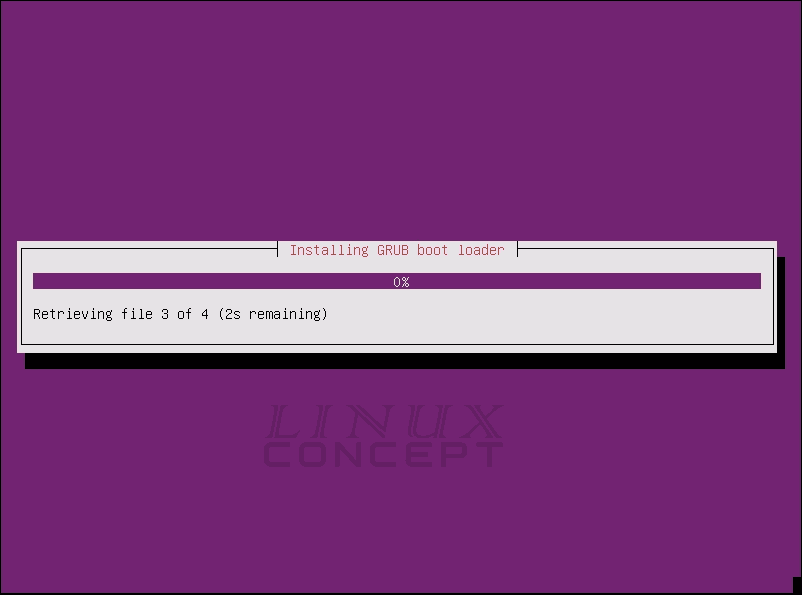
GRUB boot configuration is the last installation process of Ubuntu 16.04 operating system. After configuring GRUB it finishing the operating system installation and booting the virtual machine.
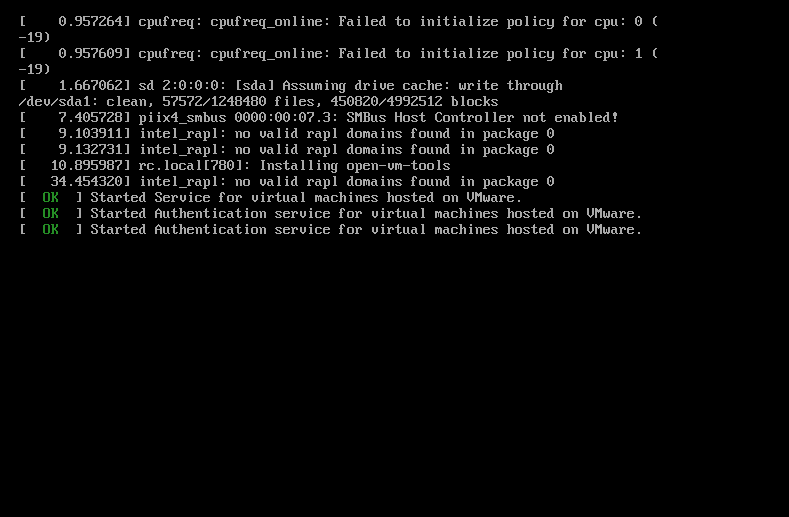
After a reboot of the virtual machine, we will get the login window on the screen where we can log in with the username and password which we had configured in the beginning of virtual machine configuration.

FAQ on VMware and Ubuntu:
How do I download Ubuntu on VMware workstation?
To download an Ubuntu Operating system on VMware is the download an ISO file of Ubuntu to install it in a virtual machine using VMware Workstation.
you can download the Ubuntu ISO file from this link: https://ubuntu.com/download/desktop
After downloading the ISO file, choose in Optical drive of VM setting and boot VM from the ISO file.
How long does it take to install Ubuntu on VMware?
Generally, it took 10-15 minutes to install the Ubuntu operating system into VMware.
But it always depends on allocated resources to Virtual Machines, Like CPU, RAM, disk, etc.
It would be best if you went with recommended hardware resources or system requirements for the Ubuntu system as mention here:
https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Installation/SystemRequirements
How do I install Ubuntu on a virtual machine?
Multiple steps need to follow for Ubuntu installation in VMware Workstation:
Step 1 – Create a Virtual Machine under VMware Workstation.
Step 2 – Download the Ubuntu ISO file to install Ubuntu into the virtual machine.
Step 3 – Go with the VM setting and choose the ISO file as an optical drive (CD/DVD).
Step 4 – Now start the virtual machine; it will boot using ISO file, and the screen will appear with the Ubuntu installation window.
Step 5 – Now, follow the instruction appear on the screen, like Disk configuration, etc.
Step 6 – Finally, it will ask you to install some important packages like SSH, LAMP, etc. if you want, you can choose using the spacebar button and hit the Enter button to proceed.
Step 7. At last, after installing all packages, your VM will reboot and get the login screen.
To follow these steps in details, you can go with this article
How do I download VMware workstation?
You can download VMware workstation from offical VMware site:
https://www.vmware.com/in/products/workstation-pro/workstation-pro-evaluation.html
Here you will get both Windows and Linux versions; You can download your one.
How do I install VMware workstation on Linux?
First, you need to download the VMware workstation Linux version from here:
https://www.vmware.com/in/products/workstation-pro/workstation-pro-evaluation.html
Now, just run the package on your Linux box to install it in 5 steps:
Step 1: Register for an account on VMware.
https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/login
Step 2 – Download VMware Workstation 14 Pro for Linux
https://www.vmware.com/in/products/workstation-pro/workstation-pro-evaluation.html
Step 3 – Make the Downloaded File Executable
sudo chmod +x ~/Downloads/VMware-Workstation-Full-14.bundle
Step 4 – Install Dependencies for VMware Workstation
sudo apt-get -y install gcc make linux-headers-$(uname -r) dkms
Step 5 – Execute the bundle file to start Installer Wizard
sudo ~/Downloads/VMware-Workstation-Full-14.bundle
Is Ubuntu for free?
Yes, Ubuntu is an Open-source Operating system running on Linux kernel.
How do I install Ubuntu on Windows 10?
You can install Ubuntu on Windows 10 using the Virtual machine. You can create a virtual machine by using VMware Workstation, VMware Player, or Virtualbox.
How long does Ubuntu take to install?
Generally, it took 10-15 minutes to install the Ubuntu operating system into VMware.
But it always depends on allocated resources to Virtual Machines, Like CPU, RAM, disk, etc.
It would be best if you went with recommended hardware resources or system requirements for the Ubuntu system as mention here:
https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Installation/SystemRequirements
What’s better VMware or VirtualBox?
If you don’t need your VM for enterprise solutions and you like it is open-source software, go with VirtualBox as your virtualization software. It’s easy to install, takes a smaller amount of resources, and is many people’s first choice.
What is Ubuntu virtual machine?
Ubuntu virtual machine is a virtual machine installed with the Ubuntu operating system and ready to use with any virtual environment provider application (VMware / Virtualbox).
What is the latest version of VMware workstation?
Currently, the latest version of VMware workstation is 16, which you can download from here:
https://www.vmware.com/in/products/workstation-pro/workstation-pro-evaluation.html
Is VMware free for Linux?
VMware Player is free for all user, either Windows or Linux.
Other products of VMware, like the workstation pro, and it is not free.
Does VMware run on Linux?
Yes, VMware providing Linux based package also to install on any flavor of Linux operating system.
Which Ubuntu version is best?
All LTS release of Ubuntu is good to use any of your purposes.
But, If you still want to know the best Ubuntu version, I’ll suggest you go with Ubuntu 16.04, and nowadays, you can also choose Ubuntu 18.04 or Ubuntu 20.04 Linux.
How do I install Linux on a virtual machine?
Multiple steps need to follow for Linux installation in VMware Workstation:
Step 1 – Create a Virtual Machine under VMware Workstation.
Step 2 – Download Linux ISO file to install Linux into the virtual machine.
Step 3 – Go with the VM setting and choose the ISO file as an optical drive (CD/DVD).
Step 4 – Now start the virtual machine; it will boot using an ISO file, and the screen will appear with the Linux installation window.
Step 5 – Now, follow the instruction appear on the screen, like Disk configuration, etc.
Step 6 – Finally, it will ask you to install some important packages like SSH, LAMP, etc. if you want, you can choose using the spacebar button and hit the Enter button to proceed.
Step 7. At last, after installing all packages, your VM will reboot and get the login screen. Yes, VMware providing Linux based package also to install on any flavor of Linux operating system.

0 Comments